Database - Introduction
An Introduction to Data, Database and DBMS along with MySQL.
Introduction
Before jumping right into MySQL, let's understand some basic terminology and some basic concepts of the data and database. After getting a concrete understanding of the basic things, we can learn about MySQL and then deep dive into it.
Data
Data refers to facts or information that can be recorded and stored in various forms. It is often used to represent facts, concepts, or instructions in a structured or unstructured format.
Data can take many different forms, including numbers, text, images, audio, and video. It can be stored in various formats, such as files, databases, or memory, and can be processed, analyzed, and visualized using a variety of tools and techniques. In computing, data can be processed by software or algorithms to produce useful information.
Types of Data
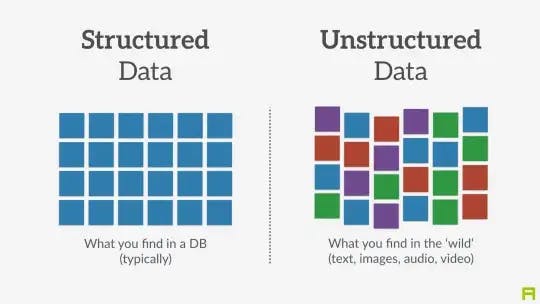
1. Structured Data
Structured data refers to data that is organized in a specific format, usually in a tabular form with rows and columns, where each column represents a specific type of data and each row represents a unique record. The data is organized in a way that allows it to be easily searched, sorted, filtered, and aggregated.
Examples of structured data include data stored in a database table, spreadsheets, and CSV files. This type of data is relatively easy to use and process because of its pre-defined schema and clear and specific column data type and names.
2. Unstructured Data
Unstructured data refers to data that doesn't have a pre-defined format or structure. It is often unorganized, and the information is not easily searchable, sortable, or analyzable. Examples of unstructured data include text documents, emails, images, videos, and audio files. This type of data is more difficult to process and analyze than structured data because it is not organized in a pre-defined format.
Unstructured data is often unformatted and can be found in various forms, such as text, audio, images, and video. It can be found in sources such as social media, email, PDFs, video, and audio recordings.
Database
A database is a collection of data that is organized in a specific way, allowing for easy access, manipulation, and management of the information. Databases can be used to store and manage a wide variety of data, including financial information, customer information, inventory, and more.
In simpler words, a Database is a container that allows us to store different types of data inside it. It's like a bookshelf, where we can organize our books. In the case of a Database, the Book is the Data and the bookshelf is the Database.
Types of Database
There are several types of databases, each with its unique characteristics and use cases. Some of the most common types of databases include:
1. Relational databases
These are the most common type of databases and store data in tables with rows and columns. They use SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and manipulating the data. Examples of relational databases include MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
2. NoSQL databases
These databases do not use a fixed schema and do not store data in tables. Instead, they store data in a variety of formats such as JSON, XML, or key-value pairs. Examples of NoSQL databases include MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis.
3. Document databases
These databases store data in semi-structured formats like JSON, BSON, etc. They are designed to store and retrieve documents, which are similar to JSON objects. Examples of document databases include MongoDB, Couchbase, and RavenDB
4. Graph databases
These databases are designed to store and manage graph data, which is data that is made up of nodes (or vertices) and edges. Examples of graph databases include Neo4j and Amazon Neptune.
There are some more types of databases like Object-oriented databases (Zope Object Database (ZODB) and Objectivity/DB) and Time-series databases (InfluxDB and OpenTSDB)
Purpose of a DBMS
DataBase Management System(DBMS) is a software or maybe a combination of multiple software that allows users to work with Data. As we already looked that, there are various types of databases to store various types of data.
A DBMS actually helps us to store, retrieve, manipulate and delete data from the database.
As we saw earlier, there are multiple types of databases that depend upon how your data looks like. To work with various types of Databases, we have various types of DBMS as well.
The most common types of DMBS are:
Relational DataBase Management System(RDBMS), which works with relational databases and uses SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and manipulating the data.
NoSQL DataBase Management System(NoSQL - DBMS), which works with NoSQL or Document Databases and uses NoSQL functional querying and manipulating the data.
MySQL is a Relational DataBase Management System(RDBMS), which works with SQL for querying. There are other RDBMS like PostgreSQL, MSSQL, and Oracle. But in this series, our main focus will be MySQL.
What's Next?
In the upcoming articles, we will talk about MySQL.
We start with MySQL introduction and how we can design a Database structure also known as Database schemas, and then how to use various types of SQL to store, retrieve, manipulate and delete data from the database.
Till then Adios. 👋

